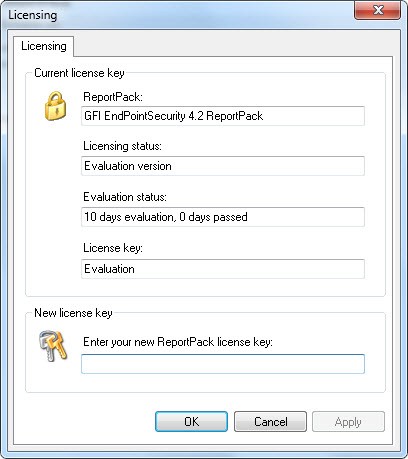
Gfi Licenses
Feb 11, 2014. This article explains the two different versions of GFI EventsManager, and how it is licensed. Unfortunately GFI doesn't break them down on its website, and. XCAPI is a software-only Fax over IP (FoIP) solution from TE-SYSTEMS. The following article explains how to install XCAPI on your GFI FaxMaker server, and how to. Aug 12, 2016 - 2 min - Uploaded by GFI SoftwareWatch this video to learn how to upgrade license keys when moving to a new version of GFI.
Trakaxpc Keygen Downloader more. Chairman/CEO Parent agency Federal Ministry of Power Website Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission (NERC) is an independent regulatory body with authority for the regulation of the electric power industry in Nigeria. NERC was formed in 2005 under the administration’s economic reform agenda through the Electric Power Sector Reform Act, 2005 for formation and review of, transparent policies regarding subsidies, promotion of policies that are efficient and environmentally friendly, and also including forming and enforcing of in the creation and use of electricity in Nigeria.
The next screen that you will encounter displays the EULA. Choose the option to accept the license agreement, and click OK. You will now see a screen asking you to enter your full name, your company name, and your license key. If you have not yet purchased a GFI EndPointSecurity license,.
NERC was instituted primarily to regulate the tariff of companies owned or controlled by the government, and any other generating company which has a license for and, and distribution of electricity. Contents • • • • • • • • History [ ] Electric power generation in Nigeria began in 1896. In 1929, the Nigeria Electric Supply Company (NESCO) was established. Malayalam Tv Serial Actress Photo Gallery. In 1951, the Electric Corporation of Nigeria (ECN) was established to take over the assets of NESCO. In 1962, NDA (Nigeria Dams Authority) was established to develop the hydropower potentials in Nigeria. In 1972, ECN and NDA were merged to form NEPA (National Electric Power Authority), which later metamorphosized to, as a holding company for its imminent unbundling and subsequent privatization.
Previously, the Federal Ministry of Power oversees the electric power sector in Nigeria. It served both as the policy making body and the regulator; doing the latter mostly through the Electrical Inspectorate Services, a department in the Ministry. The electric power sector in Nigeria started with the Niger Dams Authority which controlled the Dams around Shiroro and River Niger. Manual For Creative Model Makers Magnifying more. Due to abysmal power crises in the whole of Nigeria, the government of President made efforts through the National Council for Privatisation/Bureau for Public Service (under the leadership of to reform the sector which has seen no investment or major government attention since the 1980s. The NERC was formed through the EPSRAct of 2005 and it was inaugurated on 30 October 2007 with Ramsome Owan as its first Chairman/CEO.
Ransome Owan, a US trained scientist who once worked for GE, was appointed for a five-year term as the executive Chairman of NERC. On his team included other Nigerians living in Diaspora who came in to work for NERC.
NERC was given additional responsibilities for setting up and administering a fund called “Power Consumer Assistance Fund” which shall subsidize underprivileged power consumers in Nigeria. It also had the mandate to regulate the rural systems and determine the contribution rates to be sent to the Rural Electrification Fund. Powers and duties of NERC [ ] The Commission's powers and duties are provided for in the EPSRAct 2005, and effectively ushered the privatization of electric power services in Nigeria, unbundling of the defunct National Electricity Power Authority (NEPA)/Power Holding Company of Nigeria (PHCN).
NERC’s primary duty is protect the interests of consumers, issue licenses to operators/investors, set and review electricity tariffs and where possible promote competition. The Commission's main objective is to protect existing and future consumers' interests in relation to electricity generated and that conveyed by distribution or transmission systems. Consumers' interests are their interests taken as a whole, including their interests in affordable tariffs and safe, reliable and available electricity supply, and the reduction of greenhouse gases to them. Structure of NERC [ ] The Nigerian Electricity Regulatory Commission is governed by a tenured Board of Commissioners, headed by a Chairman. The nominates one nominee Commissioner to represent his/her geopolitical zone in the country for a fixed tenure of 4 years, renewable once only. The Chairman/CEO, has a period of 5 years, also renewable once only.
Comments are closed.